RDM Functions
As of Version 8.0, each criteria field can optionally contain a function instead of a simple expression, as previously implemented. The advantage to functions is that you can implement much more complex logic than what you can with a single expression.
If the criteria source begins with a left brace ({) the source between the braces will be compiled as a function. Otherwise, it will be treated as an expression as in previous versions. The function uses syntax similar to C++ for declarations, statements and expressions (see Syntax Diagrams).
Each function must contain at least one Return statement that will return a value back to RDM. Most criteria requires a Boolean return expression, with a few exceptions, such as Index and Variable data, which require a string.
The function code can contain:
- Variable declarations (int, uint, real, bool, string). Variables must be declared at the top of the function before any executable statements. Arrays with up to ten dimensions may be declared.
- IF statement with optional else clause.
- FOR statement.
- WHILE statement.
- RETURN statement.
- Assignment statement.
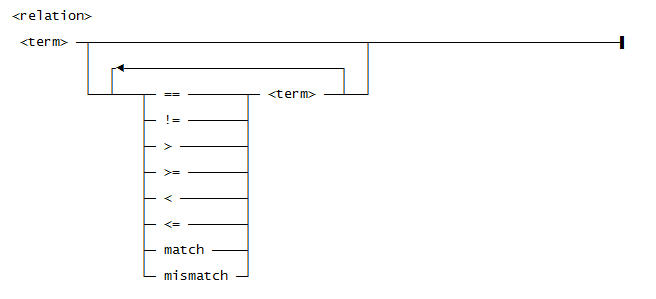
- Compare expressions, using ==, !=, <, <=, >, >=, match, and mismatch.
- Boolean expressions using &&, ||, and ! characters.
- Numeric expressions using +, -, *, /, %, ~, &, |, ^, and parentheses.
- Casting functions, such as int(xxx).
- Access to these built-in variables/functions:
| • | jtic_desc - job description |
| • | jtic_name - job name |
| • | jtic_creator - job creator |
| • | title - document title |
| • | creator - document creator |
| • | dist_id - the generated dist_id string |
| • | current_page - current page |
| • | prev_page - previous page |
| • | next_page - next page |
| • | first_page - first page |
| • | last_page - last page |
| • | page(n) - page specified by number |
| • | <page>.region_text - extract a region from the specified page |
| • | <page>.text - extract text from a specified section of a page |
| • | region.total_lines - number of lines of text in the region |
| • | region.line[n] - specified line in the region |
| • | page_number - number of the current page |
| • | <page>.page_orientation - returns the orientation of the page being referenced, in degrees clockwise (0, 90, 180, 270) |
| • | <page>.page_var - get the value of a page variable |
| • | doc_var - get a document variable |
| • | doc_inx - get the value of a document index |
| • | string_len - convert an integer value to a string with leading zeros |
| • | page_inx - get the value of a specified page index |
| • | fill - fills a string with a specified character pattern |
| • | repeat - fills a string with a repeating character pattern |
| • | pad - pads the string by adding blanks to the right (at the end) |
| • | cpad - pads the string by adding blanks at both ends so the specified text is centered |
| • | lpad - pads the string by adding blanks to the left (at the beginning) |
Example
{
int i;
string s;
s = current_page.region_text("Invoice Nums");
for (i=1; i<=s.total_lines(); i=i+1)
{
if (s.line(i) match "*9047*")
return(false);
}
return(true);
}
String Selection Criteria
The string selection criteria described in this section is only available for use with functions. They cannot be used with expression syntax. For a list of string selection criteria that can be used with both functions and expressions, see RDM String Selection Criteria.
|
Function |
Description |
|
cpad |
Pads the string by adding blanks at both ends so the specified text is centered. |
|
fill |
Fills a string with a specified character pattern. |
|
lpad |
Pads the string by adding blanks to the left (at the beginning). |
|
pad |
Pads the string by adding blanks to the right (at the end). |
|
repeat |
Fills a string with a repeating character pattern. |
|
string_len |
Converts a numeric value to a string. It sets the value to a fixed length by padding it with leading zeros. For example, if the variable n contains 123, then string_len(n,7) will return 0000123. |
Syntax Diagrams
Compiler
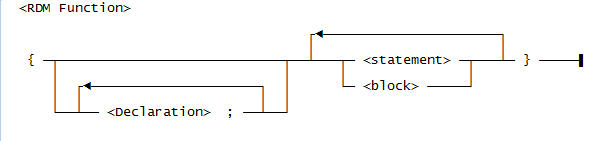
This is the general syntax for an RDM function:
Use this syntax for <line comment>:
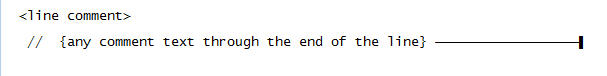
Use this syntax for <block comment>:

Declarations
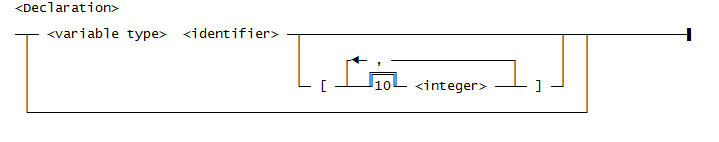
This is the general syntax for a declaration:
Use this syntax for <variable type>:

Expressions
This is the general syntax for an expression:

Use this syntax for a <boolean expression>:
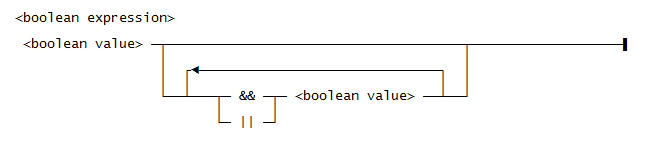
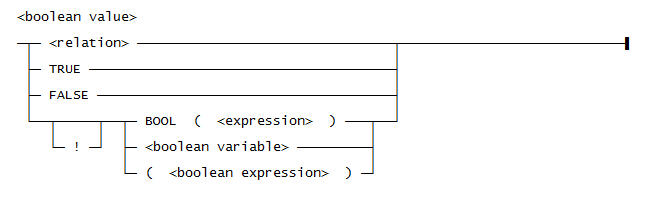
Use this syntax for a <boolean value>:
Use this syntax for <relation>:
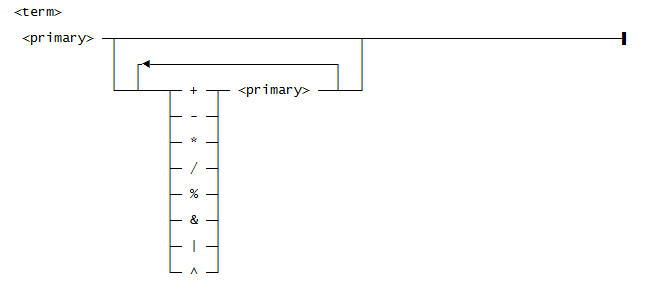
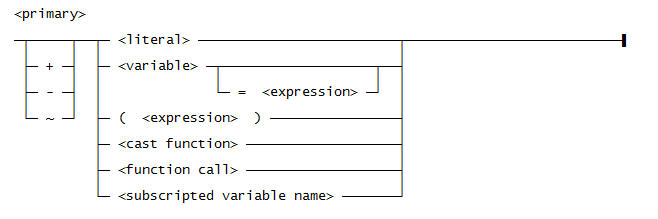
Use this syntax for <primary>:
Use this syntax for <literal>:

Use this syntax for a <string expression>:

Use this syntax for an <int expression>:
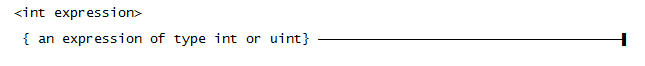
Use this syntax for a <cast function>:

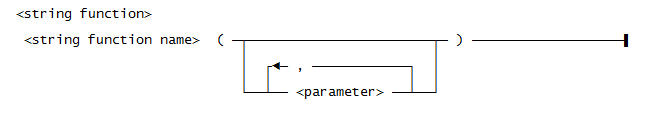
Use this syntax for a <string function>:
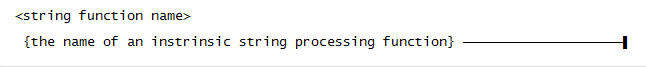
Use this syntax for a <string function name>:
Functions
This is the general syntax for a function call:
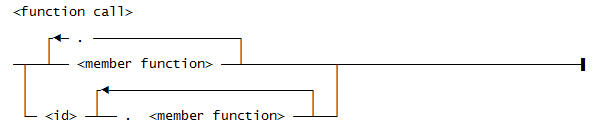

Use this syntax for <member function>:
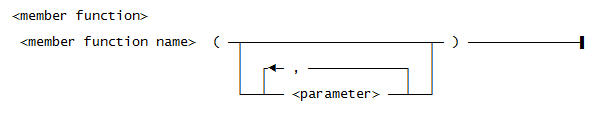
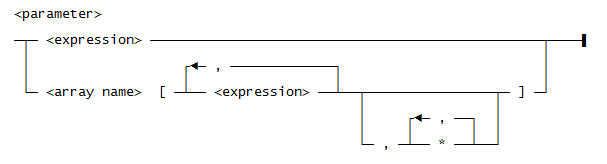
Use this syntax for <parameter>:
Use this syntax for <member function name>:

Statements
This is the general syntax for a statement:

Use this syntax for an <Assignment statement>:

Use this syntax for an <assignment expression>:

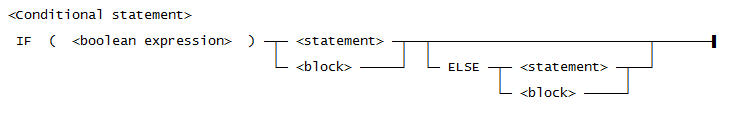
Use this syntax for a <Conditional statement>:
Use this syntax for a <For statement>:
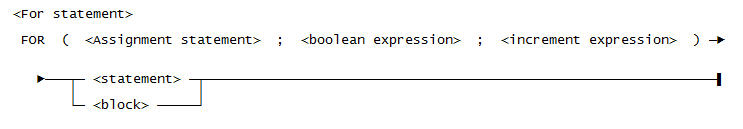
Use this syntax for an <increment expression>:

Use this syntax for a <Return statement>:

Use this syntax for a <While statement>:

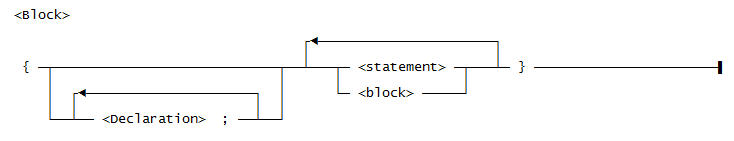
Use this syntax for a <block>:
Types
Use this syntax for a <letter>:

Use this syntax for a <digit>:

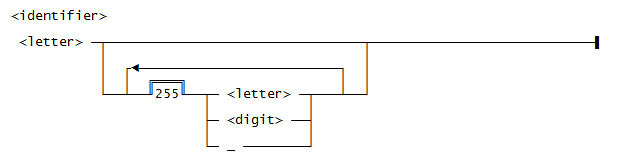
Use this syntax for an <identifier>:
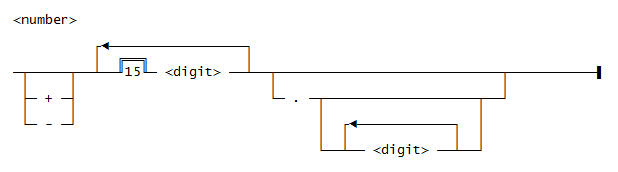
Use this syntax for a <number>:
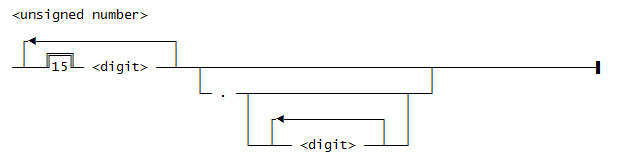
Use this syntax for an <unsigned number>:
Use this syntax for an <integer>:

Use this syntax for a <string literal>:
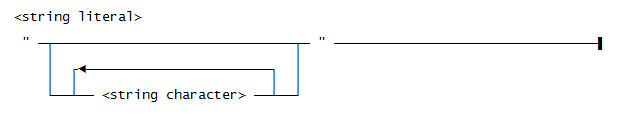
Use this syntax for a <string character>:

Use this syntax for a <variable>:
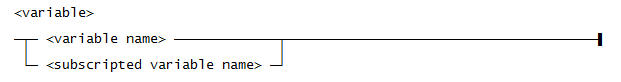
Use this syntax for a <variable name>:

Use this syntax for a <subscripted variable name>:

Use this syntax for an <array name>:

