Roles
AEO implements role-based access control. Therefore, rights to access areas of the product and rights to perform various operations are granted to roles, and not directly to users.
Users are associated with roles, either by direct assignment or by membership in Active Directory groups. As users change responsibilities within the product, their product access is adjusted by assigning or removing roles.
It is best practice to have roles own folders rather than having users’ own folders. Having roles own folders simplifies the maintenance and transition as users come and go. Users can be easily removed from the system without affecting folders and folder contents.
Role Properties
| Type | Option to have this role either grant or revoke rights. This option is only available when initially creating the role. Once the role has been saved, the role type cannot be modified. Selecting the Revoke type option will cause all role rights selected in the role to be removed from all users associated with this role. |
| Email, Phone, Other | Information available to process definitions in folders owned by the role for actions. For example, email can be automatically sent to this email address when the process fails. Only available if Role type is GRANT. |
| All Agents | Users associated with this role will have access to all agents. Only available if Role type is GRANT. |
| Exempt from timeout | Users associated with this role will be exempt from the client timing out. This is useful in a datacenter where users are monitoring the operations but are not actively touching the keyboard or mouse. Only available if Role type is GRANT. |
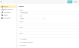
The following screen shot shows a role definition with Grant set for the type.
|
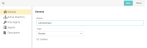
The following screen shot shows a role definition with Revoke set for the type.
|
Active Directory
Active Directory Groups can be assigned to a role. When a user logs into the scheduler, if the user belongs to any AD Group that is associated with a role, the user will be given the rights in that role. This can let Active Directory dictate what roles are associated with a user rather than directly assigning a role to a user’s record.
Role Rights
List of rights either granted or revoked in this role. Users associated with this role are either granted or revoked these rights.
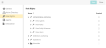
The rights for the role are organized in a tree structure:
|
A right is assigned to the role by marking the checkbox.
Assigning Rights
Role rights are additive. The total rights a user has are the cumulation of rights from all roles assigned to a user. For example, if Role A has Rights One and Two and Role B has Rights Two and Three, a user granted Role A and Role B would have Rights One, Two, and Three. To avoid creating custom roles for specific users, it is best practice to define a number of smaller roles rather than all-inclusive roles.
Revoking Rights
There are cases where a user might have too many rights because of the combination of assigned roles. Rather than redefining those roles or creating new roles to handle this situation, rights can be revoked. When a role is created, there is initially an option to revoke selected rights. Choosing that option will make it so any rights associated with this specific role will be revoked from any user assigned to it. Roles that revoke rights take precedence over roles that grant rights. Once created this way, this role will always remove
Agents
List of agents granted in this role. Users can be limited to the Agents they have access to by listing those accessible agents in this agent list. Users associated with this role are granted access to these agents. This section cannot be modified if the role type is Revoke or if the All Agents option is selected.
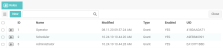
Default Roles
When the product is first installed, default roles are automatically loaded in the database. Though these roles are examples to follow and modify as seen fit, they do represent the basic user types of the product.
|
